Contrasting Kidney Stones vs UTI: What You Need to Learn About Their Impact on Health and wellness
Contrasting Kidney Stones vs UTI: What You Need to Learn About Their Impact on Health and wellness
Blog Article
A Comprehensive Analysis of Treatment Options for Kidney Stones Versus Urinary Tract Infections: What You Need to Know
While UTIs are generally resolved with prescription antibiotics that supply rapid relief, the technique to kidney stones can vary significantly based on private variables such as stone dimension and structure. Non-invasive techniques like extracorporeal shock wave lithotripsy (ESWL) might be appropriate for smaller sized stones, yet bigger or obstructive stones commonly call for more invasive methods.
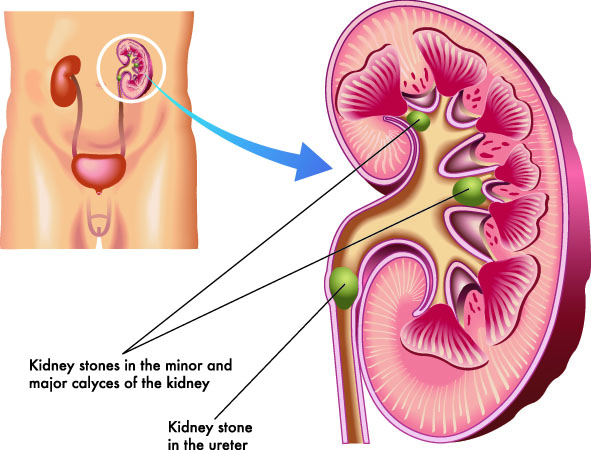
Comprehending Kidney stones
Kidney stones are difficult deposits formed in the kidneys from salts and minerals, and understanding their composition and formation is essential for effective monitoring. The primary types of kidney stones include calcium oxalate, calcium phosphate, struvite, uric acid, and cystine stones, each with unique biochemical origins. Calcium oxalate stones are one of the most typical, usually resulting from high levels of calcium and oxalate in the urine. Aspects such as dehydration, nutritional behaviors, and metabolic conditions can add to their formation.
The formation of kidney stones occurs when the focus of particular materials in the urine boosts, causing formation. This condensation can be affected by urinary pH, quantity, and the existence of preventions or marketers of stone formation. For instance, low pee volume and high level of acidity contribute to uric acid stone advancement.
Understanding these factors is crucial for both avoidance and therapy (Kidney Stones vs UTI). Reliable monitoring approaches may include nutritional modifications, enhanced liquid consumption, and, in many cases, medicinal interventions. By recognizing the underlying causes and sorts of kidney stones, healthcare service providers can apply tailored approaches to reduce reoccurrence and improve person end results
Introduction of Urinary System Tract Infections
Urinary tract infections (UTIs) are typical bacterial infections that can impact any kind of component of the urinary system, including the kidneys, ureters, bladder, and urethra. Most of UTIs are triggered by Escherichia coli (E. coli), a sort of bacteria generally discovered in the intestines. Females are much more at risk to UTIs than men because of anatomical differences, with a shorter urethra facilitating simpler microbial accessibility to the bladder.
Signs of UTIs can differ depending upon the infection's area however often consist of frequent urination, a burning sensation during peeing, strong-smelling or cloudy urine, and pelvic discomfort. In a lot more extreme instances, particularly when the kidneys are entailed, signs may also include high temperature, chills, and flank pain.
Danger elements for establishing UTIs include sex-related activity, specific kinds of birth control, urinary system system irregularities, and a weakened immune system. Medical diagnosis typically involves urine tests to determine the presence of microorganisms and various other indications of infection. Trigger therapy is vital to stop problems, consisting of kidney damages, and commonly involves anti-biotics customized to the certain germs included. UTIs, while common, require prompt acknowledgment and administration to guarantee efficient results.
Treatment Alternatives for Kidney stones
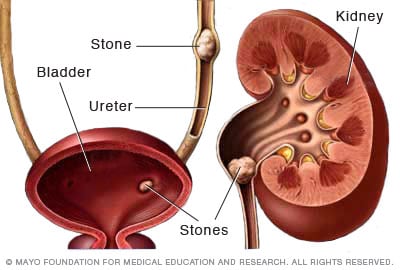
If the stones are larger or create significant discomfort, non-invasive procedures such as extracorporeal shock wave lithotripsy (ESWL) might be employed. This technique utilizes acoustic waves to damage the stones into smaller sized pieces that can be extra quickly passed via the urinary tract.
In situations where stones are also huge for ESWL or if they obstruct the urinary system system, ureteroscopy may be indicated. This minimally invasive treatment entails the use of a tiny scope to damage or get rid of up the stones straight.
Therapy Options for UTIs
Exactly how can medical care companies properly deal with urinary system infections (UTIs)? The main approach involves an extensive analysis of the individual's signs and symptoms and case history, complied with by proper analysis screening, helpful resources such as urinalysis and urine culture. These tests aid recognize the original virus and establish their antibiotic vulnerability, assisting targeted therapy.
First-line treatment typically includes prescription antibiotics, with alternatives such as nitrofurantoin or trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole, depending upon neighborhood resistance patterns. For straightforward cases, a brief course of prescription antibiotics (3-7 days) is usually enough. In recurring UTIs, companies may take into consideration alternate methods or prophylactic anti-biotics, consisting of lifestyle adjustments to minimize danger elements.
For patients with complex UTIs or those with underlying wellness concerns, a lot more aggressive treatment may be needed, possibly including intravenous anti-biotics and additional analysis imaging to evaluate for problems. Additionally, person education and learning on hydration, health methods, and symptom management plays a crucial role in prevention and recurrence.
Contrasting End Results and Effectiveness
Evaluating the results and performance of therapy choices for urinary system system infections (UTIs) is important for maximizing client treatment. The main treatment for straightforward UTIs generally includes antibiotic therapy, with options such as nitrofurantoin, fosfomycin, and trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole.
On the other hand, treatment results for kidney stones vary substantially based on stone location, composition, and dimension. this article Choices vary from conservative administration, such as hydration and pain control, to interventional treatments like extracorporeal shock wave lithotripsy (ESWL) and ureteroscopy. While ESWL has a high success rate for smaller sized stones, complications can emerge, necessitating further treatments.
Inevitably, the performance of treatments for both problems pivots on precise diagnosis and customized methods. While UTIs normally react well to prescription antibiotics, kidney stone management may call for a diverse strategy. Constant evaluation of treatment results is essential to improve patient experiences and reduce recurrence prices for both UTIs and kidney stones.
Final Thought
In summary, therapy methods for kidney stones and urinary tract infections vary dramatically due to the distinct nature of each condition. Non-invasive techniques such as extracorporeal shock wave lithotripsy are ideal for smaller stones, whereas larger or obstructive stones may require ureteroscopy.
While UTIs are commonly resolved with antibiotics that provide rapid relief, the technique to kidney stones can differ significantly based on individual aspects such this as stone dimension and composition. Non-invasive approaches like extracorporeal shock wave lithotripsy (ESWL) might be suitable for smaller stones, yet bigger or obstructive stones often call for even more intrusive techniques. The primary kinds of kidney stones include calcium oxalate, calcium phosphate, struvite, uric acid, and cystine stones, each with distinct biochemical origins.In comparison, therapy outcomes for kidney stones vary considerably based on stone location, size, and composition. Non-invasive methods such as extracorporeal shock wave lithotripsy are appropriate for smaller sized stones, whereas bigger or obstructive stones might need ureteroscopy.
Report this page